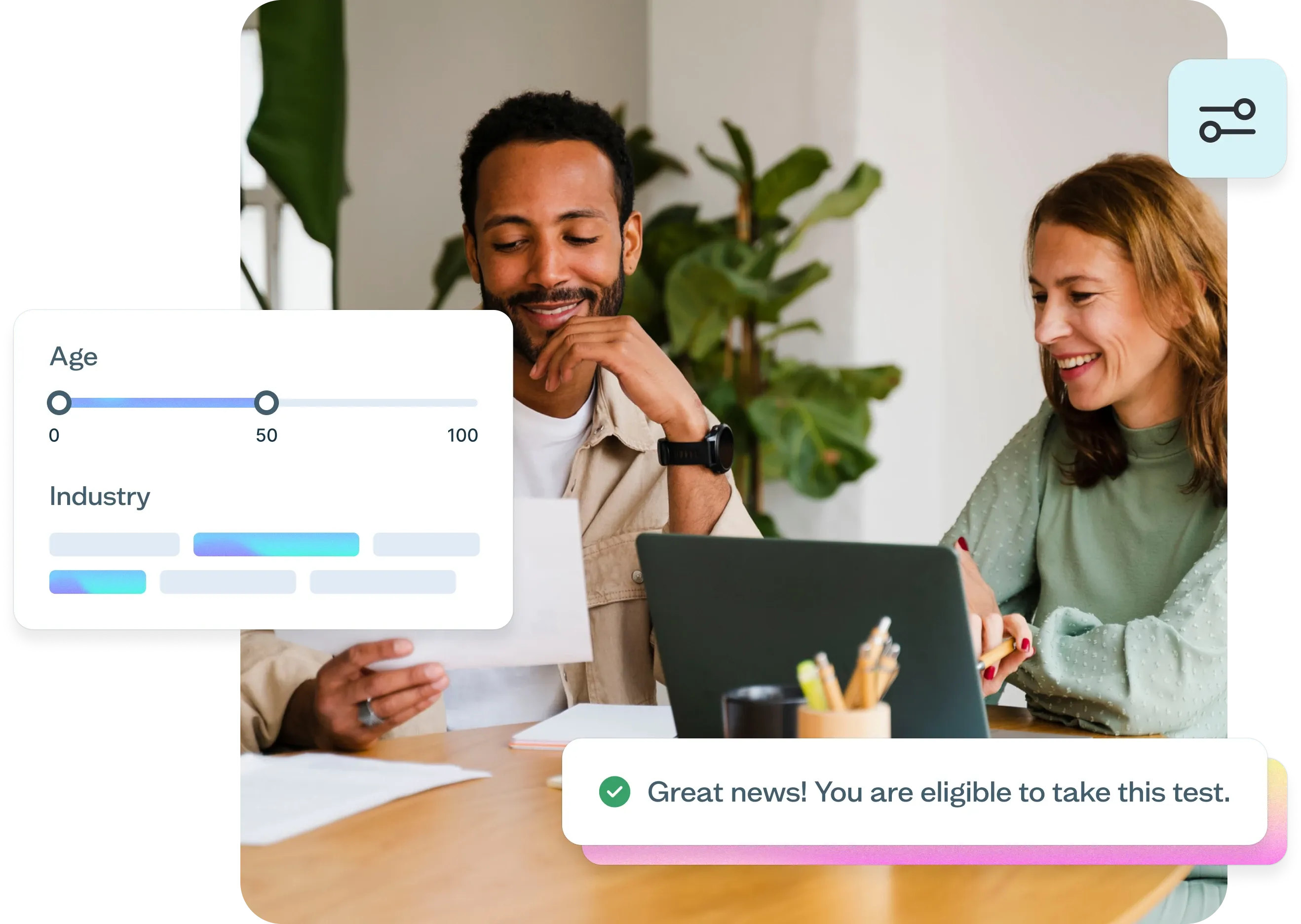
Remote usability testing
Learn what remote usability testing is, when and how to conduct it effectively, and how to use different testing methods to gather authentic user insights that drive better product decisions.
Usability testing guide
Remote usability testing has transformed how teams gather user feedback, breaking down geographical barriers and enabling more authentic insights. According to a Gartner survey, 82% of company leaders plan to allow employees to work remotely at least part of the time, making remote testing methods increasingly essential for gathering honest feedback from participants in their own environments.
This guide covers everything you need to know about remote usability testing: what it is, when to use it, and how to conduct it effectively to drive better product decisions.
Start testing remotely today
Try Lyssna free to conduct remote usability tests with real users. Get authentic feedback from your own environment in minutes.
What is remote usability testing? An overview
Remote usability testing represents a fundamental shift from traditional lab-based research, enabling teams to observe real users interacting with products in their natural environments while gathering authentic feedback about user experiences.
Definition
Remote usability testing is a method where participants test a product from their own environment while researchers observe remotely. Unlike traditional in-person usability testing conducted in controlled lab settings, remote testing allows participants to use their own devices, internet connections, and familiar surroundings while completing tasks and providing feedback.
This approach leverages digital platforms and screen-sharing technology to bridge the gap between researchers and participants, creating a more natural testing environment that often yields more authentic user behavior and honest feedback.
Testing type | Setup | Cost | Scale | Insights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Remote | Quick digital setup via platforms like Zoom or Lyssna | Lower (no travel or facility costs) | Easy to scale globally with diverse participants | Authentic behavior in natural environments; less observer effect |
In-person | Requires physical lab space and equipment coordination | Higher (facility rental, travel, equipment) | Limited by geography and scheduling | Controlled environment; direct observation of body language and reactions |
Key characteristics
Remote usability testing has several defining characteristics that distinguish it from traditional testing methods:
Conducted online via platforms like Zoom or Lyssna
Modern remote testing relies on specialized platforms that can capture screen recordings, audio, and sometimes video of participants as they interact with digital products. Some usability testing tools, like Lyssna, offer the ability to record participants' audio, camera, and screen, which can help address this issue.
Participants use their own devices
Rather than using standardized lab equipment, participants test on their personal computers, tablets, or smartphones. This provides insights into how products perform across different devices, operating systems, and screen sizes that users actually use in real life.
Sessions can be moderated or unmoderated
Remote testing offers flexibility in how much researcher involvement occurs during the session. Moderated sessions include real-time interaction between researcher and participant, while unmoderated sessions allow participants to complete tasks independently with their actions recorded for later analysis.
Why it matters
Remote usability testing enables cost-effective, scalable, and authentic insights compared to lab-based testing. The traditional model of bringing participants into controlled lab environments, while valuable for certain types of research, creates artificial conditions that can influence user behavior.
Remote testing addresses several key limitations of lab-based research:
Authentic environment: Participants test in their actual usage environment, complete with their typical distractions, device configurations, and real-world constraints. This authenticity often reveals usability issues that wouldn't surface in a sterile lab setting.
Reduced observer effect: Participants often feel more comfortable and behave more naturally when they're not being watched in person, leading to more honest feedback and typical usage patterns.
Broader accessibility: Remote testing removes geographical constraints and makes it easier for people with mobility limitations, busy schedules, or other barriers to participate in research.
Faster turnaround: Without the need to coordinate physical spaces and travel, remote testing can be set up and executed much more quickly than traditional lab studies.

5 key benefits of remote usability testing
Remote usability testing offers strategic advantages that can transform how teams approach user research and product development.
1. Wider reach and diverse participants
Remote usability testing breaks down geographical barriers, letting you connect with a global audience without physical location constraints. This provides rich, varied data from users across different demographics, cultures, and backgrounds.
Traditional testing limits you to people who can physically visit a facility—typically a narrow geographic area. This creates blind spots, especially for products intended for global or diverse audiences.
Remote testing enables you to:
Access global talent pools: Recruit participants from anywhere, ensuring research reflects your actual user base
Include underrepresented groups: Reach participants who face barriers to in-person testing—people with disabilities, parents with young children, or those in rural areas
Test across devices and environments: Observe performance on different devices, operating systems, and internet speeds that reflect real-world conditions
Capture cultural nuances: Understand how users from different backgrounds interact with your product, revealing insights crucial for international expansion
2. Cost-effective
Traditional in-person testing comes with high costs: facility rental, participant compensation, and travel expenses. Remote testing eliminates these costs, making it budget-friendly.
Key savings include:
No facility costs: Eliminates hundreds or thousands of dollars per day for dedicated testing spaces
Reduced participant compensation: Without travel requirements, participants often accept lower rates
Zero travel expenses: Neither researchers nor participants need to travel
Scalable economics: Run dozens or hundreds of sessions simultaneously across time zones without significant added costs
Faster setup: Launch tests within hours rather than days or weeks, reducing opportunity costs
3. Real-world context
Users test in familiar environments, providing natural feedback that reflects actual usage patterns. This real-world context reveals insights that controlled labs cannot capture.
What you gain:
Natural distractions: Participants experience the same interruptions they face during normal usage—phone calls, notifications, family members. These reveal how your product performs under real conditions
Authentic device usage: Participants use their own devices with customized settings and installed apps, showing how your product interacts with real environments
Typical internet conditions: Testing on actual internet speeds reveals performance issues affecting real users
Comfortable honesty: Participants provide more candid feedback in their own space, leading to honest assessments
"We used to spend days collecting the data we can now get in an hour with Lyssna. We're able to get a sneak preview of our campaigns' performance before they even go live."
Aaron Shishler
Copywriter Team Lead at monday.com
4. Scalability
Unmoderated tests let teams run many sessions at once, dramatically increasing feedback volume within a given timeframe. This becomes valuable when you need to validate design decisions quickly or test with large sample sizes.
Scalability advantages:
Simultaneous sessions: Dozens of participants can complete tasks at once, unlike one-at-a-time moderated testing
Rapid iteration cycles: Launch a test, gather results, make changes, and test again within the same day
Statistical confidence: Larger sample sizes become economically feasible, enabling statistically significant results
Time zone advantages: Global testing means participants can complete sessions around the clock
5. Flexibility for teams
Remote tools allow distributed teams to collaborate in real time, supporting modern remote and hybrid work environments. This flexibility extends to both research teams and the broader product development process.
Team benefits:
Distributed observation: Multiple team members can observe sessions from different locations without physical space constraints
Asynchronous analysis: Team members in different time zones can review recordings and contribute insights on their own schedules
Cross-functional participation: Product managers, developers, and designers can all observe sessions without logistical complexity
Documentation and sharing: Digital recordings and automated transcripts make it easier to share insights and create lasting documentation

Disadvantages of remote usability testing
While remote usability testing offers significant advantages, it's important to understand its limitations to set realistic expectations and choose the right approach for your research goals.
1. Limited contextual cues
It's harder to read body language or subtle emotional signals that provide valuable insights into user experience. In traditional lab settings, researchers can observe micro-expressions, posture changes, and other non-verbal cues that indicate frustration, confusion, or delight.
What you might miss:
Emotional indicators: Subtle signs of user frustration or satisfaction might not be captured through screen recordings alone
Empathy building: Team members observing remote sessions may not develop the same emotional connection to user struggles that comes from in-person observation
Environmental context: While you can see what's happening on screen, you might miss important environmental factors affecting the user's experience
Communication barriers: Video call fatigue and technical audio issues can make it harder to build rapport with participants and encourage open feedback
2. Technical barriers
Issues like poor internet or unfamiliarity with tools can disrupt sessions and affect the quality of data collected. Technical problems can create artificial friction that doesn't reflect actual product usability issues.
Common technical challenges:
Connectivity issues: Poor internet connections can cause lag, dropped calls, or poor audio quality that interferes with natural task completion
Platform learning curve: Participants may struggle with screen sharing software or testing platforms, creating additional cognitive load that affects their performance
Device compatibility: Different operating systems, browsers, or device configurations might cause technical issues that don't reflect real usability problems
Recording failures: Technical glitches can result in lost session data, requiring additional sessions and potentially delaying insights
If you're using a usability testing platform like Lyssna, security is handled responsibly and carefully, but teams should still prepare backup plans for technical difficulties.
3. Less control over environment
Participants may face distractions at home or in public spaces that can affect their focus and the validity of test results. While real-world distractions can provide valuable insights, they can also interfere with specific research objectives.
Potential disruptions:
Unpredictable interruptions: Family members, pets, deliveries, or other household activities can interrupt sessions and affect participant focus
Inconsistent lighting and audio: Varying environmental conditions can make it harder to observe participant reactions or hear their feedback clearly
Privacy concerns: Participants might be less willing to share honest feedback if they're concerned about family members or colleagues overhearing their comments
Multitasking temptation: Without researcher supervision, participants might be tempted to check email, respond to messages, or engage in other activities during testing
4. Recruitment challenges
Ensuring participants fit the exact persona can be harder online. Recruiting user research participants remotely often relies on self-reported information and digital screening methods rather than in-person verification.
Key recruitment issues:
Identity verification: It can be more difficult to verify participant characteristics and ensure they truly represent your target audience
Motivation and engagement: Remote participants might be less engaged or motivated compared to those who have made the effort to visit a testing facility
No-show rates: Remote sessions often experience higher no-show rates, as participants face fewer barriers to canceling at the last minute
Technical prerequisites: Participants need adequate technical setup and skills, which might exclude certain user groups from your research

Remote usability testing methods
Understanding the different approaches to remote usability testing helps you choose the right method for your specific research goals, timeline, and resources.
Moderated remote testing
Live sessions with a facilitator guiding the participant through tasks while observing and asking questions in real time. This approach maintains the interactive benefits of traditional lab testing while gaining the advantages of remote participation.
How it works: A researcher conducts the session via video conferencing software, guiding participants through predetermined tasks while observing their screen and asking follow-up questions. The researcher can provide clarification, probe deeper into participant responses, and adapt the session based on what they observe.
Moderated remote testing is best for:
Complex prototypes, exploratory testing, and situations where you need to understand the "why" behind user behavior. Moderated sessions excel when you're testing early-stage concepts, need to explore user mental models, or want to gather detailed qualitative insights.
Key advantages:
Real-time clarification and follow-up questions
Ability to adapt the session based on participant responses
Rich qualitative insights from direct conversation
Immediate problem identification and exploration
Typical session structure:
Introduction (5 minutes): Welcome participant, explain process, address questions
Background questions (5-10 minutes): Understand participant context and experience
Task completion (20-30 minutes): Guide through specific scenarios while observing
Wrap-up discussion (5-10 minutes): Gather overall impressions and final thoughts
Unmoderated remote testing
Participants complete tasks independently with recordings, providing a more scalable approach to gathering usability feedback. This method captures natural user behavior without researcher influence while enabling larger sample sizes.
Examples of unmoderated testing include five second testing, first click testing, preference testing, prototype testing, as well as screen and voice recording.
How it works: Participants receive instructions and complete tasks on their own time while their screen activity, audio, and sometimes video are recorded. They typically think aloud as they work through scenarios, providing insights into their thought processes and reactions.
Unmoderated remote testing is best for:
Quick feedback, large sample sizes, and situations where you want to minimize researcher bias. Unmoderated testing is particularly effective for testing specific task flows, gathering quantitative data, and validating design decisions with statistical confidence.
Key advantages:
Scalable to large participant numbers
Eliminates researcher bias and influence
Participants work at their own pace and comfort level
Cost-effective for gathering broad feedback
Available 24/7 across different time zones
Typical testing scenarios:
Task completion rates and success metrics
Navigation and findability issues
First impressions and initial reactions
Comparative testing between design options
Moderated vs unmoderated testing: A comparison
Choose the right method for your research goals.
Moderated testing | Unmoderated testing | |
|---|---|---|
Best for | - Complex prototypes - Exploratory testing - Understanding "why" behind behavior - Early-stage concepts | - Quick feedback - Large sample sizes - Task completion rates - Minimizing researcher bias |
Key advantages | - Real-time clarification and follow-ups - Adapt based on participant responses - Rich qualitative insights - Immediate problem identification | - Scalable to large participant numbers - Eliminates researcher bias - Participants work at their own pace - Cost-effective for broad feedback - Available 24/7 across time zones |
Sample size | 5-8 participants (deeper insights) | 20+ participants (broader patterns) |
Session length | 30-45 minutes (including intro and wrap-up) | 15-20 minutes (active testing time) |
Cost per session | Higher (researcher time required) | Lower (automated process) |
Research questions answered | - "Why did users struggle here?" - "What are users thinking?" - "How do users conceptualize this feature?" | - "Can users complete this task?" - "How long does it take?" - "What percentage succeed?" |
Best use cases | - Testing early-stage concepts - Exploring user mental models - Gathering detailed qualitative insights | - Testing specific task flows - Gathering quantitative data - Validating design decisions with statistical confidence |
Quick decision guide
Choose moderated testing if you need to understand the "why" behind user behavior or are testing complex, early-stage concepts.
Choose unmoderated testing if you need large sample sizes, quick feedback, or want to minimize researcher bias.
Mix both methods for comprehensive insights: use unmoderated for breadth, then moderated for depth.
Screen-share interviews
Users share screens while completing tasks; researchers observe and ask questions in a hybrid approach that combines elements of both moderated and unmoderated testing.
How it works: Participants share their screen via video conferencing while a researcher observes silently or with minimal intervention. This method allows for real-time observation while maintaining a more natural user experience than heavily moderated sessions.
Screen-share interviews are best for:
Prototype walkthroughs and usability flow checks where you want to observe natural behavior while retaining the ability to ask clarifying questions.
Key characteristics:
Minimal researcher intervention: Researchers primarily observe, only speaking to clarify instructions or ask follow-up questions
Natural task flow: Participants work through tasks at their own pace without constant guidance
Real-time insights: Researchers can identify issues immediately while still capturing authentic user behavior
Flexible interaction: Ability to switch between observation and conversation as needed
Asynchronous feedback tools
Tools where participants record feedback on their own time, such as video diaries or delayed response surveys, provide insights without requiring real-time coordination between researchers and participants.
How it works: Participants receive tasks or prompts and record their responses using video, audio, or text-based tools. They can complete these activities when convenient, providing feedback that researchers review and analyze later.
Asynchronous feedback tools are best for:
Concept testing and first impressions, longitudinal studies, and gathering feedback from participants across multiple time zones or with scheduling constraints.
Common formats:
Video diaries: Participants record themselves discussing their experience with a product over time
Screenshot annotations: Users capture and annotate screens to highlight specific issues or positive elements
Voice recordings: Audio feedback about specific features or overall impressions
Written responses: Detailed text feedback about user experience and suggestions for improvement

When to conduct remote usability tests
Understanding the optimal timing for remote usability testing helps teams maximize the value of their research efforts and gather insights when they'll have the greatest impact on product development.
Stage | What to test | Key benefits | Best methods |
|---|---|---|---|
Early design | Wireframes, clickable prototypes, information architecture | Prevents costly redesigns; quick iteration cycles; test multiple concepts cheaply | Unmoderated testing for large samples; moderated for exploring user flows |
Pre-launch | Onboarding flows, core features, conversion paths, error handling | Last chance to fix issues before impacting real users; doesn't delay launch | Moderated testing for critical flows; unmoderated for broad validation |
Post-launch | Feature adoption, support ticket patterns, analytics anomalies | Continuous improvement; addresses real user problems; tracks optimization over time | Mix of both: moderated for deep dives, unmoderated for tracking metrics |
Global testing | Cultural fit, translations, regional devices, local context | Understand international markets without travel costs; test with native speakers | Unmoderated for scale across time zones; moderated for cultural insights |
Early design stages
Validate wireframes or clickable prototypes before development to identify major usability issues and validate core user flows before investing in full development.
Why this timing matters: Early-stage testing prevents costly redesigns later in the development process. Remote testing is particularly valuable at this stage because you can quickly test multiple concept variations with different user groups to identify the most promising direction.
What to test:
Information architecture: How users navigate through your proposed site structure
Core user flows: Whether users can complete primary tasks with your wireframe designs
Content comprehension: If users understand your messaging and value proposition
Feature prioritization: Which proposed features users find most valuable or confusing
Remote testing advantages at this stage:
Quick iteration cycles allow rapid testing of design variations
Lower costs enable testing multiple concepts without budget constraints
Diverse participant pools provide broader perspective on design decisions
Unmoderated testing can gather feedback from large samples to validate design directions
“Lyssna is supporting us in reducing the MVP delivery timeline from 1 year to 3 months.”
Louis Patterson
Innovation Delivery Officer at British Red Cross
Pre-launch testing
Test navigation, onboarding, or checkout before release to identify and fix critical usability issues that could impact user adoption or conversion rates.
Critical focus areas:
Onboarding flows: Ensure new users can successfully complete account creation and initial setup
Core feature adoption: Test whether users can discover and use your product's main features
Conversion paths: Validate that purchase, signup, or other conversion flows work smoothly
Error handling: Identify how users react to and recover from error states
Strategic value: Pre-launch testing provides the last opportunity to fix major usability issues before they impact real users and business metrics. Remote testing's speed advantage means you can identify and address issues without delaying launch timelines.
Post-launch optimization
Identify pain points and friction in live products to continuously improve user experience and address issues discovered through user feedback or analytics data.
Ongoing optimization opportunities:
Feature adoption issues: Understand why certain features have low usage rates
Support ticket patterns: Investigate common user problems reported to customer service
Analytics anomalies: Explore unexpected user behavior patterns revealed by data analysis
Competitive response: Test how your product compares to new competitor offerings
Remote testing benefits for optimization:
Quick deployment means you can test solutions rapidly
Real-world testing environment matches actual user conditions
Cost-effectiveness enables frequent testing to track improvement over time
Large sample sizes provide statistical confidence for optimization decisions
Global testing
Ideal for products targeting multiple regions, devices, and languages, remote testing enables comprehensive international user research without the prohibitive costs of global travel.
International research advantages:
Cultural insights: Understand how different cultures interact with your product
Language testing: Validate translations and localized content with native speakers
Regional device preferences: Test on devices and platforms popular in specific markets
Local context understanding: Observe how local internet speeds, usage patterns, and environmental factors affect user experience
Practical considerations:
Time zone coordination: Plan sessions across multiple time zones to accommodate global participants
Local recruitment: Partner with local research firms or use international participant panels
Cultural sensitivity: Adapt research protocols to respect local customs and communication styles
Technical requirements: Account for varying internet speeds and device capabilities across regions
Recommended reading: How to create a usability test plan

Our 5 top tips for effective remote usability testing
These practical best practices will help you conduct more successful remote usability tests and gather higher-quality insights from your participants.
1. Set clear goals
Start by clearly defining what you want to achieve with your usability test. Having well-defined goals will guide your test design and ensure the data you collect is relevant, actionable, and aligned with your product development strategy.
Define specific research questions:
What specific user behaviors do you want to observe?
Which metrics will indicate success or failure?
What decisions will you make based on the results?
How will the insights influence your product roadmap?
Choose appropriate success metrics:
Task completion rates: Percentage of users who successfully complete key tasks
Time on task: How long it takes users to complete specific actions
Error rates: Frequency and types of mistakes users make
Satisfaction scores: User ratings of ease of use and overall experience
Conversion metrics: Whether users complete desired actions like signups or purchases
Align with business objectives:
Ensure your testing goals connect directly to business outcomes, whether that's improving conversion rates, reducing support tickets, or increasing feature adoption.
2. Recruit the right participants
Your participants should closely represent your target audience. Use screening questions to confirm they have the necessary experience or fit your target demographic. The more aligned your participants are with your actual users, the more valuable your findings will be.
Effective screening strategies:
Demographic matching: Age, location, income level, and other relevant characteristics
Behavioral criteria: Usage patterns, experience levels, and relevant product familiarity
Technical requirements: Device ownership, internet speed, and platform experience
Motivational alignment: Ensure participants have genuine interest in your product category
Recruitment best practices:
Over-recruit by 20-30%: Account for no-shows and technical difficulties
Diverse representation: Include participants across different user segments
Clear expectations: Communicate time requirements and technical needs upfront
Incentive alignment: Offer appropriate compensation that attracts quality participants
Recommended reading: Quick guide to recruiting user research participants
3. Test the tech first
Before you launch your usability test to a broader audience, run a pilot test with a small group of participants. This helps you spot any issues with your test design, like unclear instructions or technical glitches.
Technical preparation checklist
Platform testing: Verify your chosen testing platform works across different devices and browsers
Recording quality: Ensure audio and video capture meets your analysis needs
Task instructions: Test that participants can understand and follow your instructions
Backup plans: Prepare alternative approaches for common technical issues
Pilot testing process:
Internal testing: Have team members complete the test to identify obvious issues
External pilot: Run 2-3 sessions with external participants to test the full experience
Iteration: Refine instructions, timing, and technical setup based on pilot feedback
Documentation: Create troubleshooting guides for common technical issues
4. Keep sessions short
30–45 minutes ensures participants stay focused and engaged throughout the testing session. Longer sessions can lead to fatigue, reduced attention, and lower-quality feedback.
Testing method | Recommended length | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Moderated sessions | 30-45 minutes | Includes introduction and wrap-up |
Unmoderated tasks | 15-20 minutes | Active testing time only |
Screen-share interviews | 25-35 minutes | Varies depending on complexity |
Asynchronous feedback | Multiple short sessions | Better than one long recording |
Maintaining engagement:
Clear progress indicators: Let participants know how much of the session remains
Varied task types: Mix different types of activities to maintain interest
Regular breaks: Build in natural pause points for longer sessions
Focused scope: Prioritize the most important research questions rather than trying to test everything

5. Mix methods when possible
Combine moderated (depth) and unmoderated (scale) for stronger results that provide both statistical confidence and rich qualitative insights. Different methods excel at answering different types of research questions.
Strategic method combination:
Unmoderated for breadth: Use unmoderated testing to identify patterns across large sample sizes
Moderated for depth: Follow up with moderated sessions to understand the "why" behind observed behaviors
Sequential testing: Start with unmoderated testing to identify issues, then use moderated sessions to explore solutions
Parallel validation: Run both methods simultaneously to validate findings across different approaches
Complementary insights
Quantitative patterns + qualitative understanding: Numbers tell you what's happening, conversations tell you why
Scale + specificity: Broad patterns from large samples plus detailed insights from targeted conversations
Behavioral observation + attitudinal feedback: What users do versus what they say they do
Unlocking user feedback with remote usability testing
Remote usability testing represents more than just a convenient alternative to lab-based research – it's a strategic approach that can fundamentally improve how teams understand and respond to user needs.
Capturing authentic insights
Testing in real-world environments uncovers issues that lab testing often misses. When users interact with your product in their natural contexts—surrounded by their typical distractions, using their own devices, and navigating their actual internet speeds—you see challenges that artificial lab settings simply can't reveal.
Remote usability testing captures authentic insights that make a real difference:
Real conditions: See how your product performs with multitasking, distractions, older devices, and slower connections
Natural behavior: Observe how users actually interact with your product, not how they think they should
Honest feedback: Users provide more candid assessments when comfortable in their own environment
Authentic language: Hear the actual words users employ when describing their experience
These insights reveal not just what users do, but why they do it. This provides the context needed to make informed design decisions that truly address user needs.
Driving better products
Remote usability testing enables teams to reduce risks, validate designs faster, and improve customer satisfaction through more frequent and accessible user feedback. By catching problems early, you can identify usability issues before they reach production and impact real users.
The benefits compound across your development process:
Catch problems early: Identify usability issues before they reach production
Validate decisions: Confirm designs solve actual user problems, not assumed ones
Iterate faster: Quick feedback loops enable rapid improvements
Reduce waste: Prevent building features users don't understand or value
Stay competitive: Respond to user needs faster than competitors
This rapid feedback loop keeps development focused on what truly matters to users, creating a significant competitive advantage for teams that embrace remote testing methods.
The strategic value of remote usability testing
Remote usability testing represents a fundamental shift in how teams approach user research. By removing the barriers of geography, cost, and logistics, it makes user feedback accessible to teams of all sizes and enables continuous connections with users throughout the development process.
“Adopting Lyssna got us into the habit of asking our users questions before locking in decisions.”
Ron Diorio
VP Business Development & Innovation, at The Economist
This transforms user research from an occasional, resource-intensive activity into an ongoing practice that informs every product decision. When user voices remain central to development, the outcomes improve for everyone: users get products that meet their needs, and businesses see better adoption, reduced support costs, and stronger satisfaction.
Ready to gather better insights?
Start your free Lyssna account to run remote usability tests that drive product decisions. No credit card required.